Manuscript digitization projects are increasing accessibility to researchers who, for a variety of reasons, cannot access collections in person. The Manuscripts of the Muslim World project is one such exciting project to hit the scene, not least because they actively share recently digitized manuscripts on their active Twitter account. We talked to Project Cataloger Dr Kelly Tuttle about its place in the digital humanities landscape and how to use this exciting new tool.
Describe your academic background and involvement with the MMW project?
I have a PhD in Arabic from the University of Pennsylvania and use manuscripts frequently in my own research. Right after I completed the degree, I worked in a library for a year while I looked for a traditional academic job. Once I found one, I discovered that was not really what I wanted to be doing, so when this position was posted, I jumped on it. It has been great to return to library work and to see this variety of manuscripts. Every day is different and I’m learning so much. As far as what I do for the project itself, I’m the cataloguer, which means that I try to identify and describe each manuscript that is part of the project. I’m sure I make mistakes, but fortunately, there is a growing team of volunteers who are willing to contribute their advice to the project, when asked. I also produce the metadata for the digital images that appear on OPenn, an open access repository for primary source materials.What is MMW, and what is its current status
MMW stands for Manuscripts of the Muslim World (also called Muslim World Manuscripts by one of the participating repositories). It is a project supported by a 3-year Digitizing Hidden Collections grant from the Council on Library and Information Resources (CLIR) and is currently in the beginning of its second year. As the grant name suggests, it is a cooperative effort to digitize and catalog the ‘hidden’ Islamicate manuscripts held in three repositories: Columbia University, the Free Library of Philadelphia, and the University of Pennsylvania. Bryn Mawr College and Haverford College are also contributing holdings to the project. The collections were considered ‘hidden’ because many of the Islamicate manuscripts have been lingering uncatalogued in these repositories and therefore have remained largely unseen and unresearched. We hope that this grant will help make researchers, students, and other interested parties more aware of the holdings at each of these repositories and encourage their use. Since the manuscripts will also all be digitized in high quality file formats, anyone will be able to make use of these resources even if they are not able to come to the area in person. Since this is a cooperative project, there are many different players involved. Each institution has a project lead, Mitch Fraas at Penn, Caitlin Goodman at Free Library, and Kate Harcourt at Columbia along with many other support personnel who help keep everything running smoothly. Deserving of special mention here are the staff at the Schoenberg Center for Electronic Text and Image (SCETI) at Penn and the Digital Imaging Lab at Columbia, who photograph everything, as well as the Digital Content team at Penn, who make everything available on OPenn, and at Columbia who add the holdings to the Internet Archive.
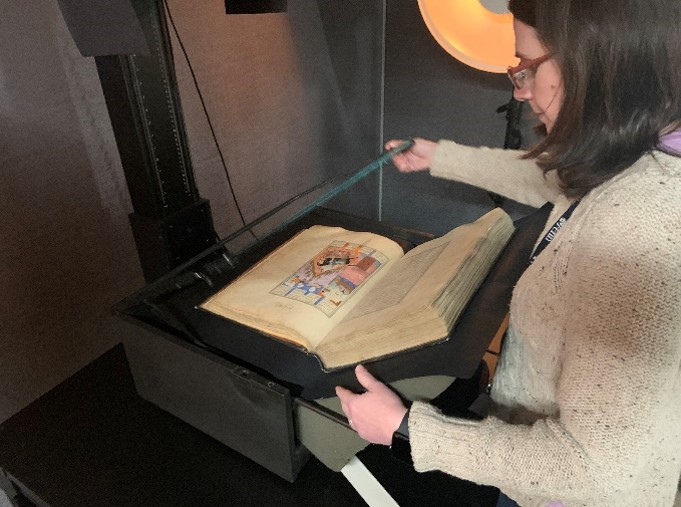

Andrea-Nunez: She is the photographer for this project at Penn. Here, she is photographing a Shāhnāmah from Free Library.
Do you have any advice for researchers who plan to use these collections?
Many of these manuscripts have been languishing unattended for a good, long while. Therefore, the time is right to poke around, find fun things to study, and bring the knowledge to the public. Browse the collections! I’m sure you’ll find something that interests you. So far, things that have stuck in my head while cataloging are that Columbia holds quite a number of teaching texts, and math and science works, in addition to some rather rare items, like a commentary in Aljamiado (Ms. Or. 515) and a forgery (Ms. Or. 388) produced in Palermo in the late 18th century. A blog post from the Columbia library gives some details about the collectors who provided most of the collection and some of what you will find in it. The Free Library has an excellent collection of illustrated manuscripts, including one illustrated version of part of the life of Emperor Akbar which is quite different from anything I’ve seen before (Lewis O 45). Penn and Bryn Mawr each have rather eclectic collections with some unique items. What immediately comes to mind from Penn is a Qur’ān that was copied in Malta (Ms. Codex 1904) and a divination book that has some fun illustrations (Ms. Codex 1898) and from Bryn Mawr a Shāhnāmah that is in an excellent state of semi-finishedness (BMC 65) with illustrations in all stages of development. Haverford has a good collection of Syriac manuscripts along with some Arabic and Persian, one of which a former owner has decorated with a number of rather awesome marginal doodles (Haverford College, Quaker & Special Collections mss. RH 66). The project is only half done, though, so more interesting things will surely be turning up!

Columbia_MsOr515: Folio 4v, Risālah, late 16th century. Text in Aljamiado, Spanish in Arabic letters.
For those of you browsing the digital collections, OPenn is a great repository, but it can look a little bare bones if you are used to the page-turning type of digital repository. With that in mind, if you go to the OPenn site you can read the introduction to find out how to use the repository and cite the works . You can then browse by repository , or, for this collection you can go to ‘Curated Collections’ and then to ‘Manuscripts of the Muslim World’ . Once you are there, you can search by Shelfmark, or browse through the holdings. The images, records, and metadata are all there for the taking. Please do help yourselves; it is all open access.
What are some challenges you’ve encountered in cataloging these manuscripts?
No one can be expert in all aspects of Islamicate manuscripts, and for a collection like this one, which is eclectic, spans 10 centuries, and covers areas from West Africa to India, I frequently run into things I’ve not seen before and for which I have very little reference. Thankfully, there is a growing set of resources for Islamicate manuscripts. There are still large areas, however, that are yet to be studied more fully. Perso-Indian manuscripts are one obvious example. I am not familiar with the tradition from my own training or research, but they exist in these particular collections in fairly significant numbers, and I am undoubtedly missing nuances of the copies and history as I catalog. Illustrated manuscripts present another type of challenge since I have had only minimal art historical training. I ask for outside help about the manuscripts with which I have difficulties, but sometimes answers are slow to come. I hope that having all the manuscripts available publicly will encourage people to get in touch with suggested revisions and improvements to the records, especially with regard to the structural metadata for illustrations. Another challenge has been with languages that I cannot read, but which form part of the collection; fortunately, volunteers have come to my rescue in cases like that. The project has been lucky, and I am extremely grateful, that so many people have been willing to donate their time and expertise when we need it. I hope the volunteers will continue to contribute their input.
What is your favorite manuscript you’ve worked on so far?
I don’t have a favorite, because there are cool things about each of the manuscripts I’ve worked on so far. I like anything that is a bit of a challenge, for which I need to do some digging. I also like anything that teaches me something new (so that is basically every manuscript out there). I also like finding connections between these manuscripts and manuscripts in other repositories, for example shared owner’s notes or stamps, or a scribe who copied one of these manuscripts and who I can actually then find listed elsewhere. The collections in the project were not built very systematically and so these connections do not often appear, so when they do, it is particularly nice. I also quite like it when the manuscripts seem like they’ve had a long, interesting life—when they have lots of marginalia, for example, or numerous owner’s notes, or tipped in notes and explanations. All of that is fun.
Could you tell us a bit about the advantages and disadvantages of working with digital images of manuscripts?
Since the project is based at Penn, I don’t actually see the Columbia manuscripts in person, for the most part. I therefore catalog their holdings from digital images and preliminary records that graduate students at Columbia have been learning to create. This has the advantage of letting me work remotely, but the disadvantage of obscuring some elements that would be noticeable in person. Knowledge of the paper is the most obvious drawback to digital images. You cannot look through a digital image as you would a piece of paper to see watermarks and laid and chain lines, for example. It is also more difficult to tell anything about the weight or texture of paper. Sometimes, it is hard to tell whether it has been blind-ruled or not. So, that’s a drawback. Another drawback is size distortion that comes about via digital images. A side effect of having all the images show up the same size on the monitor is that I sometimes lose track of whether I’m looking at a pocket-sized or a monumentally-sized Qurʾān, for example. That isn’t the fault of the digitizers or anything, and the measurements are of course provided along with the images, but it is easy to forget and think of all the books as the same size when they aren’t in front of you in person. A benefit of digital images, though, is the manipulability of them, which is to say they can be enlarged, cropped, rotated, and flicked through quickly without doing damage to the item. That aspect of digital images has been supremely useful in this project for reading small text, scribbly notes, for magnifying portions of the page for detail.
Is it possible for people to contribute to MMW?
In the sense that people can contribute their observations about the manuscripts, yes! Contribution is welcome and encouraged. Please do look at the digital images and decipher things that still need deciphering. Owner’s notes for example, stamps, other notes that were illegible to me, but might be legible to you, identifying what’s going on in an illustration so that I can update the structural metadata. In that sense, yes, we welcome contributions. In fact, if you have observations about provenance agents (owners, scribes, buyers, sellers, borrowers, lenders, readers, brokers, waqf donors/recipients, etc.) that you can identify in any of these manuscripts and you want to enter that information, along with the transcribed note, into the Schoenberg Database of Manuscripts, that would be a significant help.

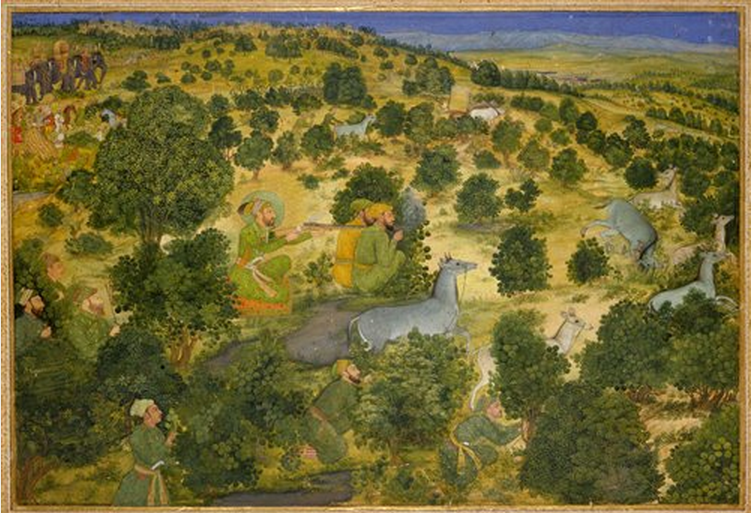
Penn_LJS405: Folio 1v, copy of Tasʹhīl al-naẓar wa-taʻjīl al-ẓafar, 14th century? This is an example of a leaf covered in owner’s notes. Help transcribing this type of thing is welcome and can be added to the Schoenberg Database by you, yourself! Please contribute.
Dr Kelly Tuttle is the project cataloger for the Manuscripts of the Muslim World grant. She is located at the University of Pennsylvania Libraries Kislak Center for Special Collections, Rare Books and Manuscripts and is reachable via email at tuttlek@upenn.edu. You can also follow the project on Twitter: @MmwProject.