Topkapı Palace Museum: Archive and Library
The Archive and Library of the Topkapı Palace Museum (Topkapı Sarayı Müzesi) contain some of the most important documents and manuscripts pertaining to Ottoman and Islamic history. The Library (TSMK) and Archive (TSMA) are both located on the grounds of Topkapı Palace in the Sultanahmet district of Istanbul.

History
Since the establishment of the palace in the fifteenth century, archival records and books have always been stored on the palace grounds. The initial storage of these materials varied over time until the establishment of the Topkapı Palace Museum in 1924. Since then, the archival materials and books of the palace have been gathered and stored in two locations on the palace grounds.
The palace archive preserves some of the oldest and most important archival records concerning the history of the Ottoman dynasty. In the earliest centuries of the dynasty’s existence, the palace (dergah-i padişahi) functioned as a movable institution constituted around the sovereign. As such, the palace’s property (including written records) often travelled with the sultan. With the establishment of Topkapı Palace at the end of the fifteenth century, the palace as institution began to assume a greater sedentary character and the records of the institution, as maintained by the Imperial Treasury (Hizane-i ‘Amire) were permanently stored on the palace’s grounds. In subsequent centuries the vast majority of these archival records were transferred to various offices of state outside of the palace. The process accelerated in the eighteenth century, so that by the time of the mid nineteenth-century establishment of a state archive (Hazine-yi Evrak), the majority of archival material was located offsite. It is this material which constitutes the historical core collections of the Ottoman Archives of the Prime Minister’s Office (Başbakanlık Osmanlı Arşivi). Today it is often difficult to discern why the material that remained at Topkapı was never transferred to various offices of state in the eighteenth century. One possible explanation is to consider the Topkapı Palace archive as the family archive of the Ottoman dynasty. In many respects this approach makes sense when we consider the large numbers of documents related to members of the ruling family and palace officials. Those records which seem more unrelated to the business of the dynasty may make some sense if we consider the ruling family’s acquisition of its servants’ property upon their death (muhallefat).
The palace’s book collection likely developed along similar lines. From the earliest periods of the dynasty’s history, learned men donated and dedicated their works to the Ottoman sultans. These works were supplemented by acquisitions from conquest and the deaths of the dynasty’s servants (whose books subsequently became the property of the ruling family). Initially these books were stored at a number of locations throughout the palace grounds. In the eighteenth century, Sultan Ahmed III established a library in the interior courtyard of the palace for the benefit of his family and the palace servants. Collection headings such as Bağdat, Revan, and III. Ahmet all refer to the original location of these works in the palace grounds.
With the establishment of Topkapı Palace Museum in 1924, the archival and library collections of the palace were entrusted to the museum. In 1925, the Ağalar Camii of the interior courtyard was converted to the New Library (Yeni Kütüphane) and the books of the various sections of the palace were moved to the new facility. In 1966, the books of the Ahmet III Library were added to the Topkapı Library in Ağalar Camii. Between 2006 and 2013 the library was closed for a number of significant renovations to Ağalar Camii. These included the construction of a new climate-controlled book depot and the restoration of the İznik tiles which decorate the walls of the library’s reading room. In August 2013, the library was re-opened and made accessible for researchers. Currently, the archive remains closed, but its staff assures us that the archive will also open in a short time.
Collections
Archive
The Topkapı collection is an indispensable source for historians concerned with Ottoman history prior to the nineteenth century. With few exceptions, the archival collection of the Topkapı Palace Museum contains the only extant official records of the Ottoman dynasty for the first two hundred years of its existence.
The archive consists of two classifications of documents: registers (defter), which range from a single sheet to several hundred pages, and loose papers (evrak), which include everything from elaborately produced letters from foreign sovereigns to scribbles on scraps of paper produced by low level palace officials. With approximately 153,000 loose papers and 10,775 registers, TSMA is the largest Ottoman archive after the Ottoman Archives of the Prime Minister’s Office (BOA). Researchers should note that the defters of the palace archive are digitally available at BOA.
In 1937 the museum invited the Hungarian historian and archivist Lajos Fekete to survey the palace archive and make recommendations for the collection’s classification. With his recommendations, the museum staff produced a two volume guide to the collection organized alphabetically according to the subject of the document (usually the document’s creator or addressee). Unfortunately this published guide only covered the archive’s collection up through the letter H. Between 1949 and 1951 M. Çağatay Uluçay described the remainder of the collection in five handwritten notebooks which were kept at the archive for researchers’ use. Beginning in 1957 İsmail Hakkı Uzunçarşılı and subsequently Şefi Ülkü Altındağ produced a catalog of the 153,000 loose papers of the archive on small notecards. These notecards and the published and unpublished guides from the first-half of the twentieth century remain the only resources which describe the full extent of the archive’s collection. Since 2006, the archive has been closed to facilitate a number of changes, foremost of which is the development of a completely new and thorough catalog of the archive’s collections. As of autumn 2013, the Archive under the direction of Sevgi Ağca has produced four volumes of a planned fifteen volumes. The volumes have been published and are available at the Archive for consultation.
As the archive of the Ottoman dynasty, the collection provides the best material for researchers concerned with the activities of the royal family, as well as the functioning of the palace and central state administration. The loose papers include all manner of official documents including edicts (ferman), titles of investiture (berat), reports (arıza), and petitions (arzuhal). The majority of the registers include finance records such as salary registers of palace officials, inventories of the Imperial Treasury, and surveys of religious endowments (evkaf) established by one of the royal family members.
Although the majority of the documents are in Ottoman Turkish, the collection also includes a fair amount of material produced in other languages. This is particularly true for the earlier periods in which much of the state correspondence was composed in Persian. The collection even includes an example of an extremely rare edict (yarlığ) in Uyghur-script Eastern Turkish (Chaghatay) composed by order of Sultan Mehmed II in the aftermath of the Ottoman victory over the Aqquyunlu confederation at the Battle of Otlukbeli in 1473.
While the vast majority of the archive’s collection consists of documents produced by the Ottoman state, the archive also includes an exceptionally important collection of documents produced by other Muslim dynasties. The majority of these documents were produced in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries by Iranian dynasties such as the Timurids, the Qaraqoyunlu, the Aqqoyunlu, and the Safavids. In all likelihood these ‘foreign’ archival documents arrived in Istanbul with other spoils of war in the wake of one of the victorious Ottoman campaigns waged against the Aqqoyunlu or Safavid polities.
Library
The collection of the palace library contains approximately 13,400 manuscripts. The majority of these manuscripts are in Arabic (approximately 8,500), although the library has a sizable collection of manuscripts in Turkish (3,081 including works in Chaghatay and Kipchak), and Persian (904). While the library is not even the largest collection in Istanbul, its holdings are distinguished by many rare and, in some cases, unique manuscripts, including many early copies of important works and a number of autographed manuscripts. Beginning in 1961, Fehmi Edhem Karatay produced a seven-volume catalog of the library’s Arabic, Persian, and Turkish collections organized according to the language and literary genre of each work. In addition to works in these languages, the library also has a sizable uncataloged collection of material in European languages. For those interested in the Greek, Latin, Armenian, and Syriac holdings of the library, we suggest consulting D. Adolf Deissmann’s Forschungen und Funde im Serai (Berlin-Leipzig, 1933).
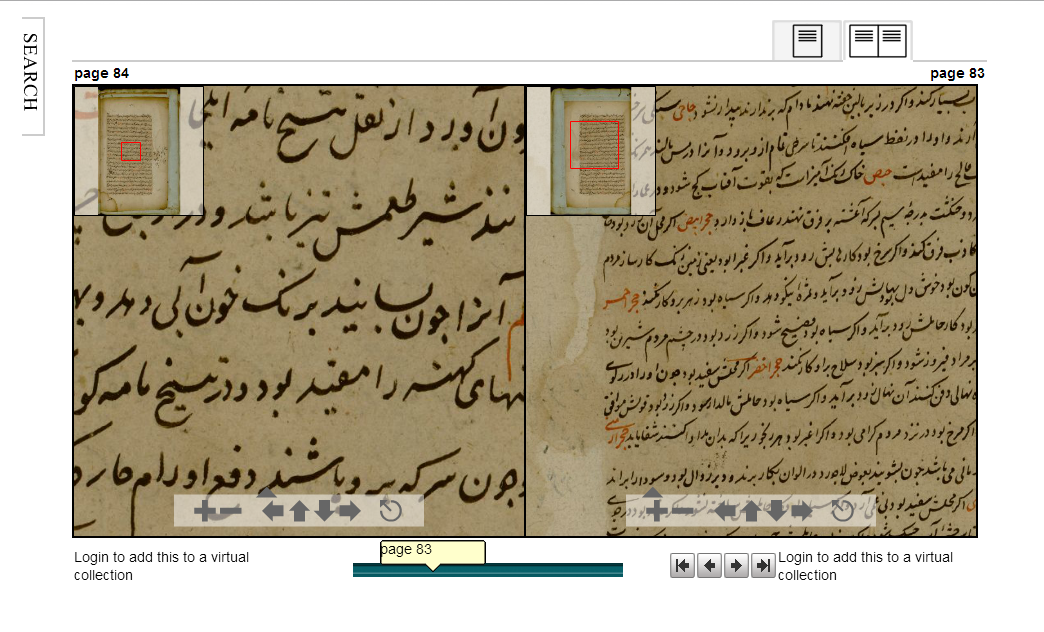
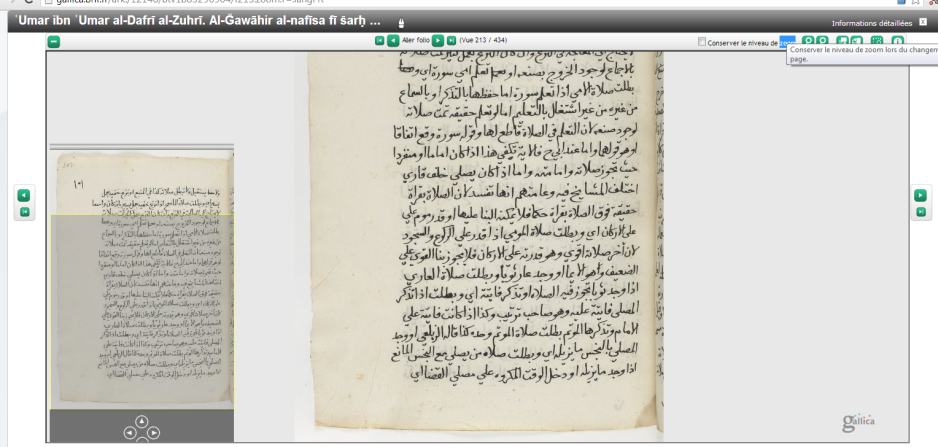
The majority of the library’s collection consists of works related to Islamic religious sciences along with many works of history, grammar, poetry, belles lettres, and other sciences. Its Arabic works are distinguished by a large number of early copies of the Quran, including a few which were reportedly copied by ‘Uthman bin ‘Affan and ‘Ali bin Abi Talib. The library’s Turkish works include a large number of histories of the Ottoman dynasty, many of which are preserved solely through the library’s copy.
While the library is certainly of great importance to historians and scholars of Islamic studies, the library’s significant collection of finely produced volumes and illustrated manuscripts mark it as one of the great libraries in the world for art historians. Most of the volumes with miniatures were produced in the palace painters’ atelier (nakkaşhane) or in Iran and subsequently acquired by the dynasty. In addition to the illustrated volumes, the library also has an important collection of calligraphy (hat) and other art forms.
Research Experience
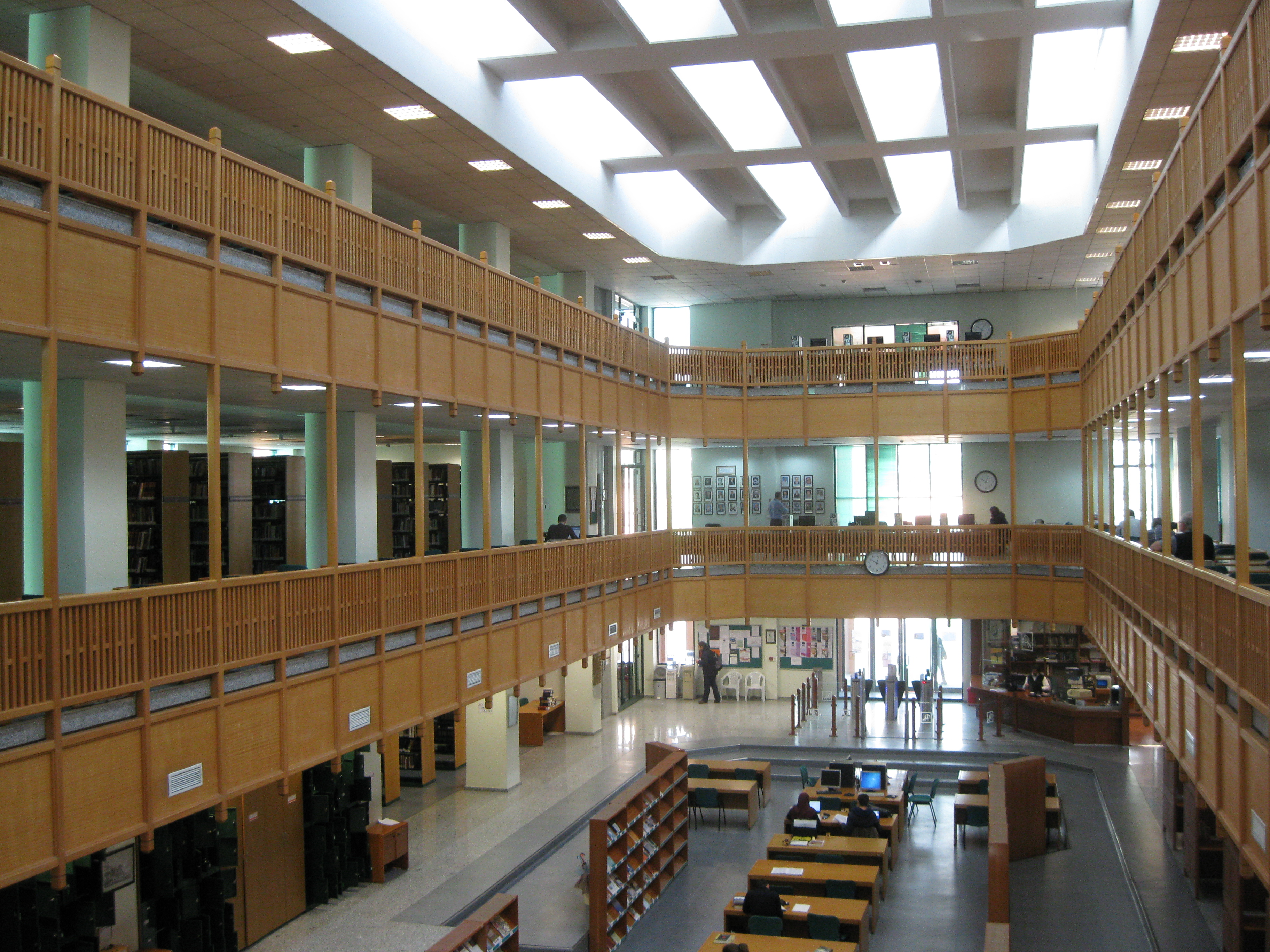
Topkapı’s library is a pleasant place to work. The library’s reading room is located in the anteroom of the former Ağalar Camii. The room consists of two large tables at which researchers may examine manuscripts. The reading room has sufficient natural light for reading and is enclosed on four side by walls of beautifully decorated seventeenth-century İznik tiles. As library patrons work in the library after making an appointment (see Accessibility section below for details on this procedure), the reading room is never crowded. Researchers request manuscripts from the library staff by submitting a short request form. Generally the staff make requested manuscripts available within ten minutes of a request. Researchers are asked to wear gloves while examining any of the library’s manuscripts.
The reading room has a complete copy of Karatay’s seven-volume catalog of the collection. The reading room’s copy of the catalog is more accurate than other copies, as it includes a number of marginal notes and corrections which detail the actual location and state of the library’s collection. In addition to these catalogs, the reading room also has a catalog key which converts the collection shelf mark number to Karatay’s catalog accession number. This catalog key is an extremely useful tool for locating references to manuscripts in Karatay’s catalogs. Aside from these materials, the library has no readily accessible reference material.
The only difficult aspect of working at the Topkapı library is negotiating the crowds of tourists on the palace grounds. As the palace is one of the most popular tourist sites in Turkey, researchers must contend with the thousands of tourists who enter the palace every day. When entering the palace grounds at the Gate of Salutation (Bab-i Selam), we advise researchers to head straight to the guard booth at the gate and present themselves as a researcher at the library. The guard will ask you to pick up a visitor’s card (ziyaretçi kartı) from the guided tours ticket sales booth. With this card, researchers may enter the palace grounds without purchasing a ticket.
While the archive is currently closed, researchers may request to purchase digital archival material if they know the archival reference number and the material has already been digitized. Requests for purchase are submitted to the archive’s director and are generally approved and ready for pick up within one week (see Reproduction section below).
The staff of the library and archive are quite friendly and willing to help. Some of the staff speak English, so researchers without Turkish should be able to manage.
Accessibility
Researchers must obtain permission to conduct research at Topkapı from the Museum Directorate. The research request application consists of a request form, a research statement produced by the researcher which describes his or her research and specifies the material at the archive or library the researcher requests to consult, a letter of affiliation with a research institution, and a photocopy of the researcher’s identification (passport or Turkish national id card). The research statement should include 1) a description of the current project on which the applicant is working, 2) mention of the purpose of the study (doctoral dissertation, academic article, etc.), 3) enumeration of the specific works or archival materials to be examined, and 4) the contact information and signature of the applicant. These applications are processed within a few days. The museum offers research permission valid for a single calendar year; each January permission must be renewed with a new application.
The library is open Monday through Friday between 9:00 and 16:00 with a one hour break for lunch between 12:00 and 13:00. After obtaining permission, those who wish to work at the library should make an appointment by telephone or in person. Researchers in wheelchairs will have some difficulty navigating the palace ground and the three steps at the library entry.
Reproduction Requests and Costs
Researchers working in the library may request digital reproductions of material upon submission of a short request form. In general, if these requests are for non-commercial scholarly use, they are quickly approved within one or two days. Reproductions of non-illustrated pages cost 2 TL for foreigners per photographic exposure and half as much for Turkish nationals. Reproductions of illustrated material cost more.
Digital reproductions of archival material may be obtained in a similar manner. As with the library, these reproductions also cost 2 TL per photographic exposure. As the archive is currently closed, researchers must know the defter or evrak reference number of their documents in order for their requests to be processed. After researchers have obtained research authorization, they may request reproductions remotely. Once the museum receives payment via bank transfer, the staff will mail copies of the requested material on CD.
Transportation and Food
The museum is in the very center of Istanbul and easily accessible by tramway. Researchers can disembark at either the Sultanahmet or Gülhane tramway stop and then proceed to the palace on foot. The approach from Sultanahmet is a bit further but is on relatively level ground, whereas the Gülhane approach necessitates a short walk up a hill.
There are few options for food on the grounds of the palace. Konyalı is the only restaurant on the grounds of the palace. It has a beautiful terrace with views of the Bosphorus, but meals here are relatively expensive. Researchers may find many options for lunch outside of the palace, but they will need to re-enter the palace grounds—and contend with the masses of tourists—when they return. We recommend packing a lunch and finding a bench to eat in one of the palace’s gardens.
Contact Information
T.C. Kültür ve Turizm Bakanlığı Topkapı Sarayı Müzesi Müdürlüğü
Sultanahmet, Fatih / İSTANBUL
Tel: +90 212 512 04 80 / Fax: +90 212 528 59 91
Email: topkapisarayimuzesi@kulturturizm.gov.tr
Resources and Links
http://www.topkapisarayi.gov.tr/
The English version of this site only includes tourist information. We recommend that researchers use the Turkish version of the site to learn more about developments at the archive and library.
Written by Christopher Markiewicz
10 October 2013
Cite this: Christopher Markiewicz, “Topkapı Palace Museum: Archive and Library,” HAZİNE, 10 October 2013, https://hazine.info/2013/10/10/topkapiarchiveandlibrary/