Written by Kelly Hammond
Introduction
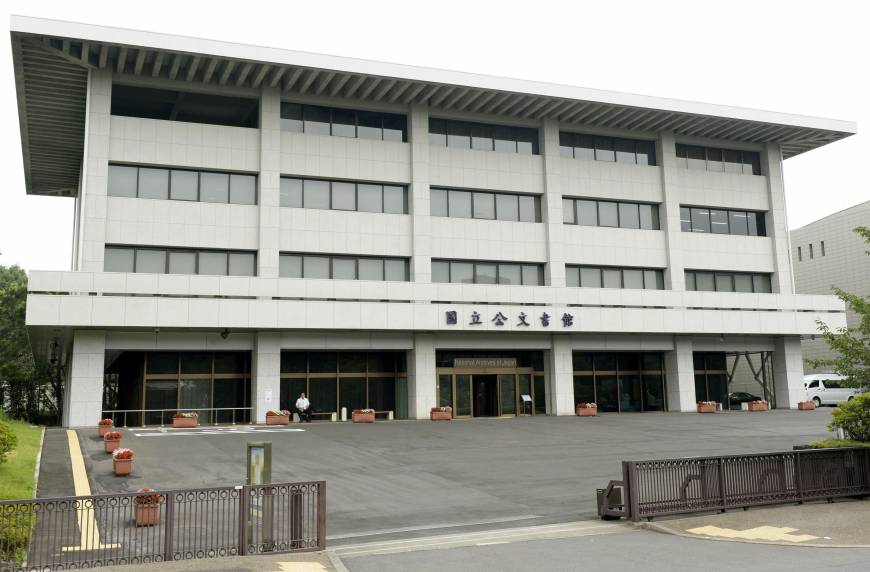
The National Archives of Japan (Kokuritsu kōbunsho-kan 國立公文書館) are invaluable to researchers working on Japan’s relationships with and growing interest in the Middle East and Ottoman Empire in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The archives are located in the Imperial Palace complex in Tokyo’s Chiyoda District at the north end of Kitanomaru Park, the former site of Edo Castle and the seat of the Tokugawa Shogun (1603-1867).
Researchers interested in the important relationships between Pan-Asianism and Pan-Islamism, non-western expressions of transnationalism and internationalism in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, and Japan’s growing scholarly interest in Islam at the turn of the twentieth century will find these archives invaluable for their research.
History
The National Archives of Japan houses most the of administrative documents of the government, as well as many journals, newspapers, manuscripts, and important books published since the Meiji Period (1868-1912) or collected by different governments since that period. During the Allied Occupation of Japan, the Diet acknowledged the need to create a permanent facility to prevent the further destruction and disbursement of documents, and to ensure that they would be made available to the public. However, it was not until 1971 that the Diet voted to establish the National Archives to ensure the preservation of government documents and publications, and to ensure that they would all be housed in one, central location. This brought together many disparate collections, such as the library for the cabinet of the Meiji government, which included seminal works of ancient Japanese and Chinese philosophy not found anywhere else. In 2001, the National Archives opened its current location and is home to the majority of surviving documents regarding decisions made by the central government.
Researchers should be aware that the Ministry of Foreign Affairs maintains its own archive and library, holding all diplomatic documents from the end of the Tokugawa Bakufu in the mid-nineteenth century until the postwar period. For anyone working on foreign relations with Japan, it is imperative that they visit this collection as well.
Collection
The archive holds government documents and publications that are available to the public from the establishment of the Cabinet system in Japan to the early 1970s. The archives also house the Momijiyama Library (紅葉山文庫), which began as the library of Tokugawa Ieyasu in 1602. This library contains maps, manuscripts, and books collected by the government from the Tokugawa Bakufu onwards, as well as important Chinese works on East Asian medical traditions, politics, plays, and early Qing Dynasty (1644-1912) novels and poetry.
However, the collections that researchers will find the most valuable are the materials compiled by the Diet starting in the Meiji Period. These document collections are arranged chronologically and classified into categories, such as public works, education, and foreign affairs. Here, researchers will find detailed works on the history of Islam and Muslim societies, detailed ethnographic studies of Muslim populations in the Middle East, India, Central Asia, and China, and reports of Japanese efforts to enlist the support of Muslims in the prewar and war periods. They will also find documents pertaining to Japan’s plans to position itself as the “Mecca of the East,” the building of the Tokyo Camii, the naturalization of Muslim Tatar refugees from the Crimea after the Russia Revolution, as well as journals and papers chronicling the conversion of numerous Japanese scholars to Islam following their studies in Istanbul and Cairo. All of these together make up one of the most important collections of works in Japanese concerning Islam.
Documents up to the end of WWII are open and public, although an archivist must screen many documents from the post-war period before they are made available to researchers. The screening process can take time, so if you plan to look at documents from 1945 onwards, inquire with the archives before visiting. Having never had to request a document that needed to be screened, I am relying on information provided on the archives website which explains that they will screen up to five documents a day per person and notify the researcher once the documents have been screened and cleared for viewing.
The Research Experience
The collection is completely searchable online by keyword, although researchers must be physically present at the archives to request documents or to view the majority of the digitized documents. Searches can be narrowed to include certain years or reigns. Researchers are advised to spend time trying numerous keyword combinations to optimize search results. They should also try kanji, hiragana, katakana and the other spelling variants. For instance, if looking for documents pertaining to “Turkey” in Japanese, it is advisable to search kanji (土耳其), hiragana (とるこ), katakana (トルコ), and any other spelling variants you are familiar with to maximize the number of hits.
There are also paper catalogs in the research room that are worth examining to cross-reference online searches, as they sometimes yield sources or avenues to researchers that online catalogs do not. Discrepancies or anomalies between the online and paper catalogs are rare, although occasionally the printed editions provide information not available in the online catalogs. Given the efficiency of the online catalog, researchers can spend a few days before they visit the archives searching the documents they would like to see or have pulled when they arrive. This allows researchers to hit the ground running: you can have a document in hand within an hour of arriving at the archives.
Japan is at the forefront of archival digitization and you can browse all of their digital holdings online (see website below). The quality of digitization is extremely high, and in my experience, there was no need to request the original if the digital copy was available. Many of the digitized documents are only available to view or print from within the archives. Some manuscripts and journals that are available widely can be downloaded from an outside network, but most documents require the physical presence of the researcher at the archives—even if the material is digitized. Printing digitized copies is free.
Pulling items that have not been digitized requires that researchers complete a form and submit it to the incredibly helpful staff. Although the staff only speak Japanese, they are extremely polite, patient, and thoughtful. After submitting a request, you can expect to see your first documents within an hour, and the archivists pull documents throughout the day, depending on the number of requests. The research room is well lit and well air-conditioned. There are some dictionaries and encyclopedias for reference use. Recently, the research room has been equipped with Wi-Fi for researchers, which is easily accessible in a few simple steps.
Access
The archives are open Monday to Friday, 9:15 to 17:00. They are closed on weekends, Japanese national holidays, and December 28-January 4 for New Year holidays. Last admission to the archives and the last time to submit a request for documents is thirty minutes before closing.
Upon arrival at the archives, you will need to register using either your passport or a valid form of government identification issued by your home country, such as a driver’s license. The process is simple and efficient and takes no more than ten minutes. Following this, researchers must sign in with a security guard who issues them a locker key to secure their belongings for the day. All government buildings in Japan are wheelchair accessible.
Reproductions
Until recently, the archives did not allow photographs, and copying was expensive. However, the archives have recently amended their regulations and now allow researchers to photograph most documents. Many Meiji (1868-1912) documents cannot be photographed, whereas most Taishō (1912-1926) and Shōwa (1928-1989) documents can. A word of advice: the National Archives holds a number of important manuscripts and journals about Islam and Islam in Asia published in the first half of the twentieth century. It is advisable to check the catalog of the National Archives of Japan before you pay to copy them at other locations (for instance at the Waseda University Library, Tōyō Bunko, or the National Library of Japan) since they may be photographed at the archives for free. This only applies to a few books and publications, but it is worth looking into since copying materials is often prohibitively expensive in Japan.
If the documents you want cannot be photographed, expect to fill out a form requesting one of the staff to copy them for you (researchers are not allowed to copy their own documents). This can take anywhere from a couple of hours to a few days, depending on the number of pages you request. Researchers can also request PDFs and/or JPEGs of their documents, which are digitized on a CD ROM for a nominal fee. Each page costs upwards of 35 US cents (or around 30-35 Japanese yen) to copy, so having the time to make good choices about what you want to copy is important.
Transportation and Food
The easiest way to get to the archive is by metro. The closest metro stop is Takebashi 竹橋 on the Tōzai Line. The next closest stop, Jinbōchō 神保町, is a kilometer walk from the archives and is on the Hanzōmon, Mita, and Shinjuku lines. As an aside, Jinbōchō is the used book district in Tokyo, and many hours can be spent meandering its small, winding streets and incredible used bookstores. Depending on where researchers are staying in Tokyo, it will cost between US $8-12 per day getting to and from the archives by metro. Researchers who are planning to stay in Tokyo for longer periods can also buy a bicycle, which is a pleasant and affordable way to get around the city. There is bike parking at the archives, or nearby at the Tōzai metro station.
There is no cafeteria in the archives, although there is a small lunchroom that researchers are welcome to share with the staff. The room has some large armchairs for quick post-lunch naps, but they are rarely vacant. Researchers can also use the vending machines and hot water dispenser in the lunchroom. Given the location of the archives at the north end of the Imperial Palace complex, there are few affordable places to eat in the surrounding areas. The archives are situated next to the National Museum of Modern Art, which has a lovely, yet rather expensive, coffee shop. A few small restaurants serving bento boxes and meal combos (teishoku) can be found within walking distance, but they are also quite expensive for lunch. The best and most affordable option for those who do not bring their own lunch are the numerous convenience stores (konbini) that are located within a kilometer or so radius from the archives. As anyone who has spent time in Japan will know, the konbini offers a very viable and affordable option for a quick lunch.
Future Plans and Rumors
The archives are constantly taking documents out of circulation for digitization. On my last visit, I was not able to see two or three documents that I ordered because they were being digitized. This slight inconvenience, however, should not deter researchers—I was able to see about 95% of what I requested.
Contact Information
3-2 Kitanomaru Park, Chiyoda District, Tokyo
東京都千代田区北の丸公園3番2 号
Telephone number: 03-3214-0621
Resources and Links
Searchable Digital Archive Collection (Japanese)
Searchable Digital Archive Collection (English)
Valuable tool for researchers to do some preliminary planning before their trip:
Kosugi Yashishi, Hayashi Kayoko and Tonaga Yasushi, eds. Islamic World Research Manual.Nayoga: Nagoya University Press, 2008.
小杉泰、林佳世子、東長靖、編. イスラム世界研究マニュアル. 名古屋:名古屋学生時代出版社、2008.
Kelly Hammond is a doctoral student at Georgetown University. Her work focuses on the Japanese efforts to win the hearts and minds of Muslims in North China during the China War (1931-1945).
21 April 2014
Cite this: Kelly Hammond, “The National Archives of Japan for Scholars of the the Middle East,” Hazine, 21 April 2014, https://hazine.info/2014/04/19/national-archives-japan/