Written by Anat Mooreville
The American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee, known as the JDC or the Joint, is an international Jewish philanthropic organization started after the First World War to assist Jewish refugees in Eastern Europe and Palestine. With records of activities in over ninety countries dating from 1914 to the present, the JDC Archives are a significant resource to understand not only American Jewish relief efforts abroad, but also Jewish social, cultural, political, and economic conditions around the world. For the Middle East, the JDC Archives include records created primarily between 1940-1977 from Aden, Algeria, Cyprus, Egypt, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Lebanon, Libya, Morocco, Palestine, Syria, Tunisia, and Turkey. Middle East specialists will find this archive particularly useful for conducting research on Jewish history in the Middle East and North Africa in the second half of the twentieth century. The archive has two locations—Jerusalem and New York City.

Collection
The JDC Archives are located in two centers, one at the JDC’s New York City headquarters and the other in Jerusalem in the Givat Sha’ul neighborhood. These centers are not equal in size and scope. The Jerusalem archive is the larger and more comprehensive of the two; in fact, all the records of the New York archive are available in Jerusalem in microfilm format.
The archive in Jerusalem houses the records of JDC field offices throughout Europe, Africa, and Asia, along with the records of JDC operations in Israel. The bulk of the Middle Eastern and North African records of the JDC are part of the Geneva Files (1945-1977), which were subsequently shipped to the JDC Archives in Jerusalem after the Geneva Office—opened in 1957 as the European headquarters of the organization—was closed in 1977.
Although this review focuses on the Jerusalem archives, I will briefly outline what is available in the New York collection. The New York archive houses American headquarters communications with governments, national and international agencies, and JDC field offices. The bulk of the archival record concerns relief, rescue and support activities in Europe between 1914 and 1945. Later materials concern JDC activities in the Displaced Persons (DP) camps of Germany, Austria, and Italy, and JDC activities in Eastern Europe during the Communist period. For the Middle East historian, the New York archives detail the medical, educational, vocational and relief activities in Palestine starting in 1914 through the Second World War. These include institutions established to help the disabled and orphans. A detailed list of these files are available online through the finding aids (search by country). They also contain information on refugee and aid activities in North Africa during the Second World War.
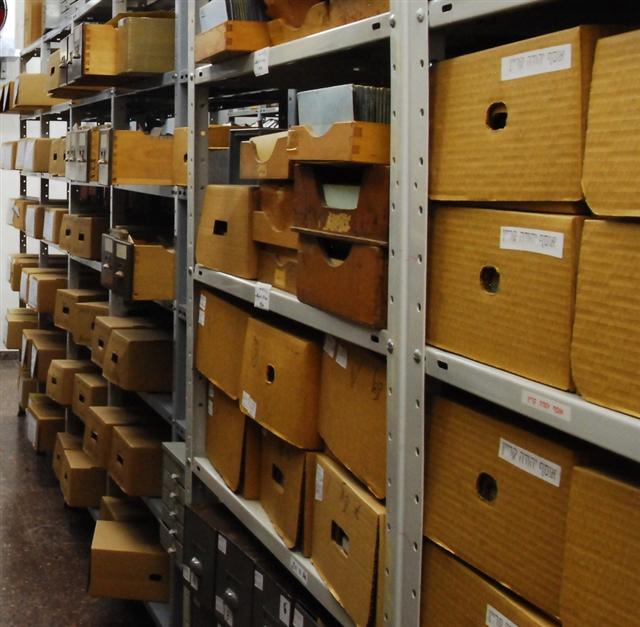
The JDC Archives includes over three miles of text documents, 100,000 photographs, a research library of more than 6,000 books, 1,100 audio recordings including oral histories, and a collection of 2,500 videos, covering 90 countries throughout the twentieth century. Many of the collections are arranged chronologically, others by subject or office of origin (e.g., Geneva, Rome, Istanbul). At the same time, the JDC is an active Jewish humanitarian assistance organization. All JDC historical records older than thirty-five years are open to the public with the exclusion of materials containing information that the JDC believes would adversely affect its ongoing work.
For the period following the founding of the State of Israel, the JDC Archives in Jerusalem contain files related to Malben (נֶחֱשָׁלִים בְּעוֹלִים לְטִפּוּל מוֹסְדוֹת “Institutions for the Care of Disabled Immigrants”), the social service organization created jointly by the JDC, the Jewish Agency, and the Israeli government in 1949. Malben provided institutional care and social services; established hospitals, clinics and old-age homes; trained nurses and rehabilitation workers; and fostered the development of private and public organizations in Israel for the care of the disabled. Files also document missions and programs to help settle Jews from North Africa and the Middle East in Israel. For example, the JDC organized Operation Magic Carpet, which evacuated about 48,000 Jews from Yemen to the newly established State of Israel and Operation Ezra and Nehemiah, which brought approximately 120,000 Iraqi Jews to Israel.
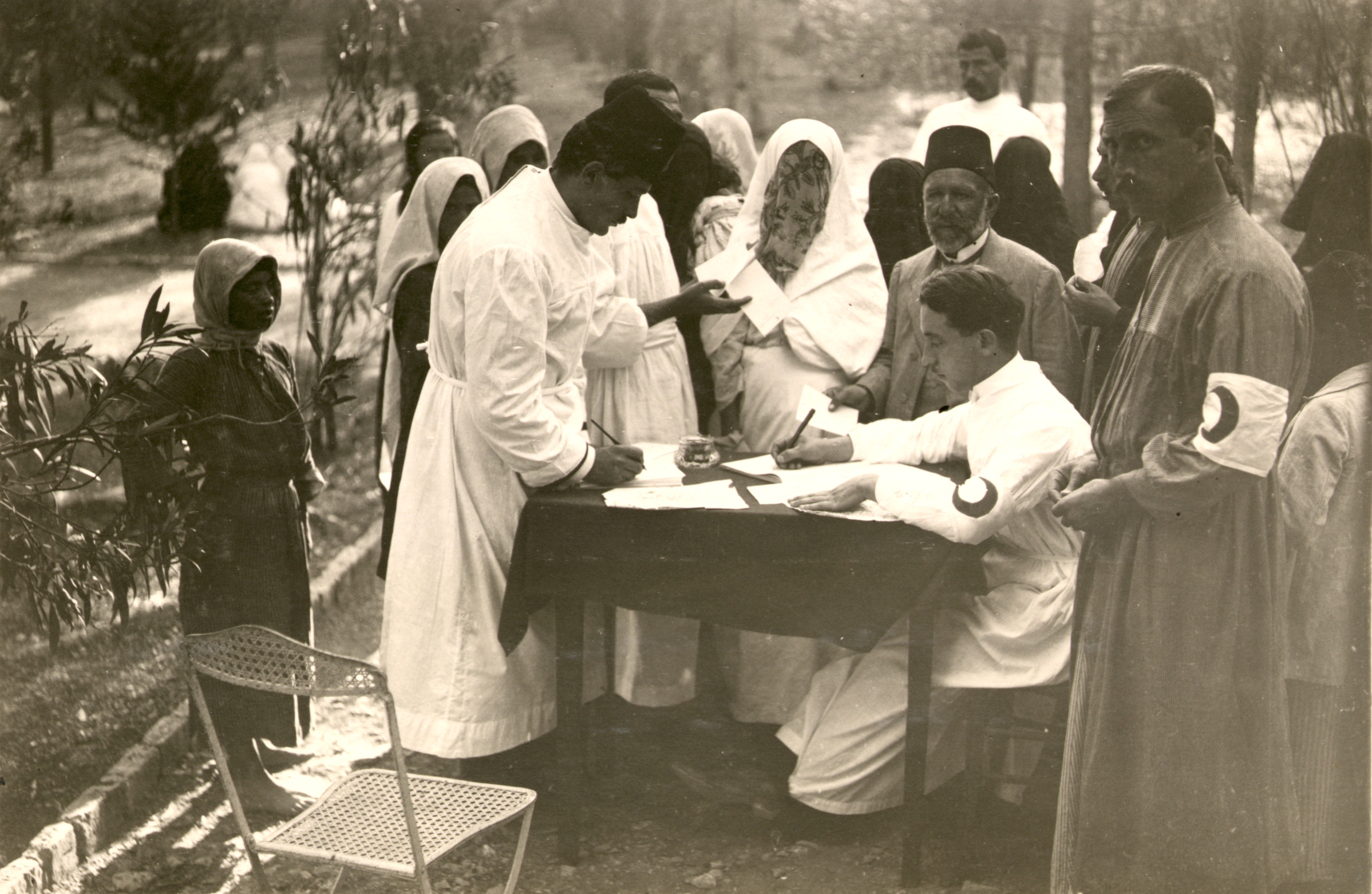
Records related to the Middle East and North Africa document the JDC’s medical, educational, and vocational support in these regions from the late 1940s through the 1970s. These social efforts were wide-ranging and expansive. In North Africa, JDC initiated public health programs with OSE (Œuvre de secours aux enfants) to combat diseases such as tuberculosis and trachoma. The JDC frequently offered assistance to local Jewish educational organizations such as Ozar Hatorah and Alliance Israelite Universelle. Numerous country reports document local demographic, economic, political, and social conditions from the perspective of the JDC’s staff.
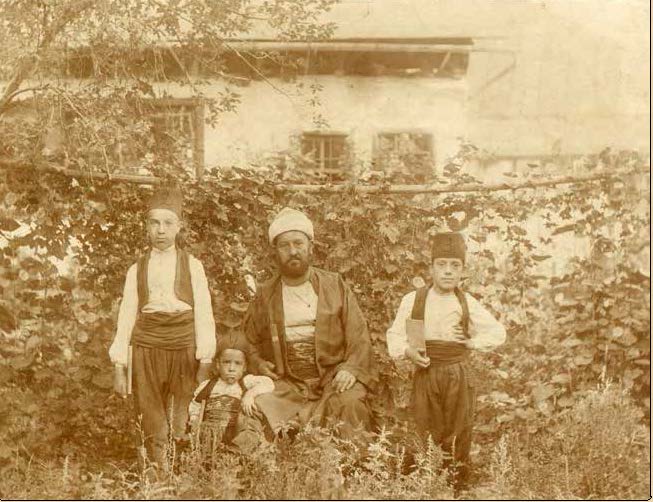
The photography collection of the Middle East and North Africa is quite large and can be fully searched by title, description, date, subject, location, photographer, and other fields on the JDC Archives’ online catalog. To see the range of photographs available, we recommend the galleries on Algeria in the 1960s, Tunisia in 1950s, and early Palestine.
A sampling of the range of materials available in the JDC archives include correspondence, committee and board meeting minutes, field reports from worldwide staff, financial statements; memoranda, lists of aid recipients and supplementary allocations, program descriptions, passenger lists, cables, supply lists, restitution laws and statutes, summaries of statistical reports, personnel files, legal files, case files, conference proceedings, lists of names, audits, brochures, press releases, pamphlets, and news clippings.

Research Experience
The JDC Archives is in the process of digitizing its collections. While the photo database is fully available online, other text resources are only partially available. The online catalog is a good place to begin your search, and some documents can be accessed through the website directly, but keep in mind it is in no way exhaustive, especially for Middle Eastern material. There is a very brief finding aid for the Geneva Office of the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee 1945-1954 records, but it does not detail the Middle East/North Africa collection. The records of the Istanbul office (1943-47) or the Geneva office (1955-1978) are not available online. You can learn more about how to search the online database by viewing the archive’s video tutorials or reading its guide. The JDC Archives staff has access to a more comprehensive online catalog that is password protected.
To access the full catalog of the JDC Archives in Jerusalem, one must first e-mail Shachar Beer to make an appointment to visit. Only one or two researchers are allowed at a time, as the archive is located in one of the working offices of the JDC. On your first visit, Mr. Beer will give you a stack of binders that contain the full catalog. Unfortunately, they are not arranged by country, and it is advisable to spend the first day examining all the binders for relevant material and noting the title and file code that you wish to order during subsequent visits. Researchers should note that since March 2013 the archive has been in the midst of reclassifying its files and consequently the code which appears on the physical file may differ from its new classification. You therefore may not be able to order material on your first day. Material can only be ordered once a day and is limited to five or six boxes (more if the material is microfilmed). These should be ordered in the morning or emailed to Mr. Beer before your visit. The time of retrieval of material is not routine, but it usually arrives from the warehouse before 11:00. Once requested, it usually takes about thirty minutes to an hour for material to be prepared for the researcher. One should also coordinate with Mr. Beer the time of arrival to the archives in the morning, which can be as early as 9:00 or as late as 11:00, depending on his schedule.
Since the JDC Archive in Jerusalem only accommodates one or two researchers per day, I would recommend allotting at least a few days for research to get the most of out of your scheduled visits. It takes some time to become familiar with the full holdings because they are not online, and one can only see a limited number of files per day.
There is one microfilm machine, as well as a spare office and a conference room in which Mr. Beer directs researchers to work with original files. The catalog does not indicate whether the file exists in microfilm or only as an original. Since the archives are in the office of a working NGO, it is mainly full of JDC staff, the archivist, and perhaps one other researcher.
Access
In order to visit the archives, one must fill out an application located online. Once permission is received (usually less than a week), you need to email Mr. Beer to schedule an appointment.
Although the stated hours of the Jerusalem Archive are Sunday-Thursday 9:00-15:00, the actual hours depend on the appointment times scheduled with Mr. Beer. Generally, researchers may work at the archive until the JDC office closes around 16:00.
Reproductions
Reproduction services (photocopy and microfilm printing) are not available. You are allowed to use a digital camera to photograph files and microfilms. There is a one shekel fee for each photograph. Researchers tally their own photographs and report them to Mr. Beer at the end of each session. In some cases, Mr. Beer will waive the fee for photographs of microfilm material.

Transportation and Food
The archive is located in the industrial park neighborhood of Givat Sha’ul in West Jerusalem. It is not easily accessible from downtown Jerusalem. Buses 33 and 67 stop outside the archive, and it is about a ten minute walk from the Kiryat Moshe light rail station.
There are many chain restaurants and cafes in the archive building and nearby that cater to the business crowd. There is free coffee and tea in the archive itself. You can also bring your own lunch and eat it in the archive.
Miscellaneous:
The JDC Archives offers a fellowship to conduct research in either the New York or Jerusalem Archives. Check the website for details and application.
Future Plans and Rumors
The archive is in the midst of digitizing its collection, so the state of the online catalog and available digitized files is constantly changing.
Contact information
JDC Archives
Beit Hadefus Street 11, Lobby 2, Floor 3
02-653-6403
General information: Archives@jdc.org.il
Archivist: Shachar Beer <ShacharB@jdc.org.il>
Resources and Links
The online catalog is sophisticated and contains 900,000 digitized pages. However, it is not complete, especially in regards to Middle Eastern and North African materials.
The archives website is quite expansive and details the history of the JDC, the archives, and contains various finding aids and resources on how to search the archive.
**Information about the history and holdings of the collection comes from the JDC Archives website.
Anat Mooreville is a doctoral candidate in the UCLA History Department where she studies twentieth-century Jewish and Middle Eastern medical history.
Cite this: Anat Mooreville, “The American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee Archives (Jerusalem), HAZINE, 2 Feb 2014, https://hazine.info/2014/02/02/jdc/